Overview
Since anatomic MRI is presently not able to directly discern neuronal loss in Parkinson’s Disease (PD), studying the associated functional connectivity (FC) changes seems a promising approach toward developing non-invasive and non-radioactive neuroimaging markers for this disease. While several groups have reported such FC changes in PD, there are also significant discrepancies between studies. Investigating the reproducibility of PD-related FC changes on independent datasets is therefore of crucial importance.
The data are comprised of 27 PD patients and 16 age-matched normal controls in the Neurocon dataset, and 20 PD patients and 20 age-matched controls in the Tao Wu dataset. Both sets contain T1 and resting-state scans.
Experimental Protocol
For the resting-state scan, subjects were instructed to close their eyes and think of nothing in particular without falling asleep.
Scan Parameters (Click here for scan parameters in BIDS format)
| Parameter | NEUROCON | Tao Wu | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1.5-Tesla Siemens Avanto MRI scanner | Siemens Magnetom Trio 3T scanner | ||
| T1-weighted scan | Sequence | MPRAGE (IR method) | MPRAGE (IR method) |
| Repetition time (TR) | 1940ms | 1100ms | |
| Echo time (TE) | 3.08ms | 3.39ms | |
| Voxel size | 0.97 x 0.97 x 1 mm | 1 x 1 x 1 mm | |
| Resting-state scan | Sequence | Echo planar | Echo planar |
| Repetition time (TR) | 3480ms | 2s | |
| Echo time (TE) | 50ms | 40ms | |
| Flip angle | 90° | 90° | |
| Voxel size | 3.8 x 3.8 x 5 mm (without slice gaps) | 4 x 4 x 5 mm (64 x 64 matrix, 28 slices, field of view=256mm x 256mm) | |
| # of Volumes | 137 (8.05 min) | 239 (8 min) |
Data Release Download
Data for the Parkinson's dataset are available for download in an Amazon Web Services S3 bucket.
Each file in the S3 bucket can only be accessed using HTTP (i.e., no ftp or scp ). You can obtain a URL for each desired file and then download it using an HTTP client such as a web browser, wget, or curl. Each file can only be accessed using its literal name - wildcards (i.e. "*") will not work.
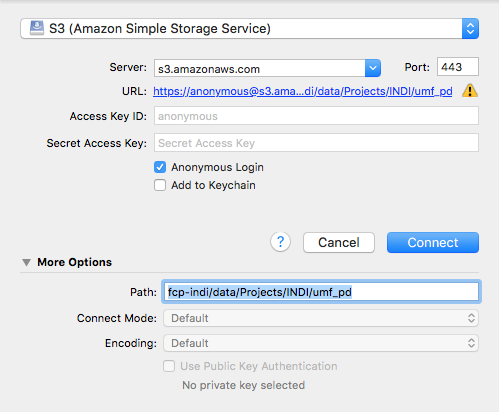
There are file transfer programs that can handle S3 natively and will allow you to navigate through the data using a file browser. Cyberduck is one such program that works with Windows and Mac OS X. Cyberduck also has a command line version that works with Windows, Mac OS X, and Linux. Instructions for using the Cyberduck program are as follows:
- Open Cyberduck and click on Open Connection.
- Set the application protocol in the dropdown menu to S3 (Amazon Simple Storage Service).
- Set the server to s3.amazonaws.com.
- Check the box labelled Anonymous Login.
- Expand the More Options tab and set Path to fcp-indi/data/Projects/INDI/umf_pd.
- Click Connect.
Personnel
Neurocon
- Liviu Badea1*
- Mihaela Onu2,3
- Adina Roceanu6
- Ovidiu Bajenaru6,7
* Please send any correspondence to badea.liviu@gmail.com
Tao Wu
- Tao Wu4,5*
* Please send any correspondence to wutao69@gmail.com
- Artificial Intelligence and Bioinformatics Group, National Institute for Research and Development in Informatics, Bucharest, Romania
- Medical Imaging Department, Clinical Hospital Prof. Dr. Th. Burghele, 20 Panduri Street, Bucharest, Romania
- University of Medicine and Pharmacy “Carol Davila”, Biophysics Department, Bucharest, Romania
- Department of Neurobiology, Key Laboratory on Neurodegenerative Disorders of Ministry of Education, Beijing Institute of Geriatrics, Xuanwu Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing, China
- Beijing Key Laboratory on Parkinson’s Disease, Parkinson Disease Centre of Beijing Institute for Brain Disorders, Beijing, China
- University Emergency Hospital Bucharest, Neurology Department, Bucharest, Romania
- University of Medicine and Pharmacy “Carol Davila”, Department of Clinical Neurosciences, Bucharest, Romania
Acknowledgements
This work was partially supported by the NEUROCON project (84/2012), financed by UEFISCDI.
Publications
Badea L, Onu M, Wu T, Roceanu A, Bajenaru O (2017) Exploring the reproducibility of functional connectivity alterations in Parkinson’s disease. PLoS ONE 12(11): e0188196. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0188196
Usage Agreement
Creative Commons License: Attribution Non-Commercial Share Alike (CC BY-NC-SA)

